Facebook handles over a billion requests per second. Not a million – a billion. Every second, their servers deal with profile loads, news feeds, photos, messages, and thousands of other actions happening simultaneously across the planet.
That’s the reality Facebook faces every second. If their servers had to fetch your profile picture from the database every time someone scrolled past it, the system would crash.
So, how do they do it? The answer is a free open-source tool called Memcached.
Memcached is the behind-the-scenes hero. It doesn’t just store data; it uses in-memory caching to store the most frequently accessed information – like your profile picture, session data, or popular product prices – directly in the server’s ultra-fast memory (RAM). This eliminates the need for slow trips to the hard drive, ensuring a seamless experience for users worldwide.
But this isn’t just for tech giants. If you want your website to handle more traffic, run faster, and avoid crashing under pressure, Memcached is your solution.
Let’s explore how this simple memory booster delivers such powerful results.
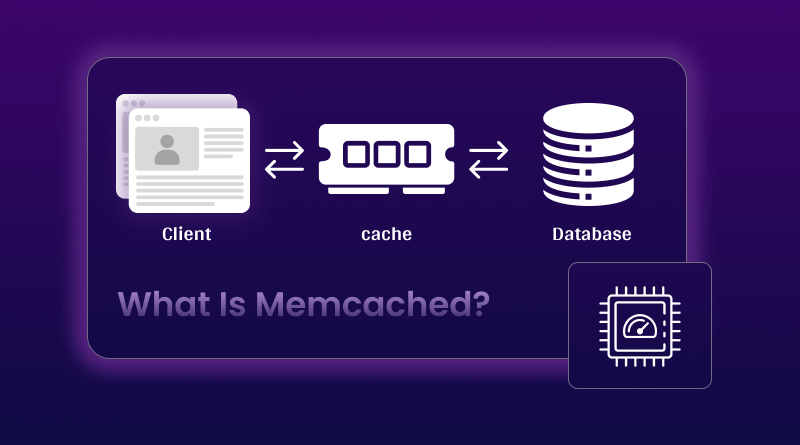
What is Memcached and How Does It Work?
Memcached is an open-source, distributed memory caching system that stores data as key-value pairs in RAM instead of on disk. Think of it as a high-speed storage layer sitting between your application and database.
How Memcached Actually Works
When your application needs data, here’s what happens:
Step 1: Check Memcached first
Before hitting the database, your app asks: “Do you have data for this key?”
Step 2: Cache hit or miss
- Cache hit: Data exists in RAM – delivered in microseconds
- Cache miss: Data doesn’t exist – fetch from database
Step 3: Store for next time
On a cache miss, your app fetches data from the database, then stores it in Memcached with an expiration time (TTL).
Step 4: Automatic cleanup
When memory fills up, Memcached automatically removes the least recently used (LRU) items.
This simple cycle can reduce database load by 70-90% for high-traffic sites.
Key Technical Features
-
Distributed Architecture
Memcached runs across multiple servers using consistent hashing to evenly distribute data. Add more servers as traffic grows without code changes. - In-Memory Speed
Storing data in RAM means read/write operations occur in microseconds rather than milliseconds. That’s 100-1000x faster than disk-based databases. - Simple Commands
Just five core operations: get, set, delete, add, and incr/decr. Most developers implement basic caching in under an hour.
Is Memcached Better Than Redis?
This question shows up constantly in searches. Neither is universally better—it depends on your specific needs.
| Feature | Memcached | Redis |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Sub-millisecond | Sub-millisecond |
| Threading | Multi-threaded | Single-threaded |
| Data Types | Strings only | Lists, sets, hashes, sorted sets |
| Persistence | None (RAM only) | Optional disk storage |
| Replication | No built-in support | Built-in replication |
| Best For | Simple caching at scale | Complex data structures |
Choose Memcached when:
- You need pure speed with simple key-value storage
- Multi-threaded performance matters
- Session storage or database query caching
- You don’t need data persistence
Choose Redis when:
- Data must survive server restarts
- You need complex data types (lists, sets, pub/sub)
- Built-in replication is required
- Advanced features like Lua scripting matter
For basic web application caching, Memcached is simpler and often faster. For more complex needs, check our Redis caching guide.
What is Memcached Used For?
Let’s look at real-world scenarios where Memcached shines.
1. Database Query Result Caching
The most common use case. Cache expensive queries to prevent them from running repeatedly.
Example:
Your homepage shows “Top 10 Products” – a query that joins three tables and takes 80ms. With 10,000 hourly visitors, that’s 800 seconds of database work for identical data.
Solution:
Cache the results for one hour. The first request takes 80ms; the next 9,999 requests take <1ms from Memcached.
2. Session Data Storage
Web applications need fast access to login state, shopping carts, and user preferences.
Why Memcached works:
- Sessions are temporary data (perfect for RAM-only storage)
- Lightning-fast reads/writes across distributed servers
- Horizontal scaling for growing user bases
Many WooCommerce hosting setups use Memcached for session management during checkout – keeping cart data accessible across multiple servers.
3. API Response Caching
External APIs are slow and often rate-limited. Cache responses to cut latency and costs.
Example:
Weather API takes 300ms and limits you to 1,000 daily calls. Cache responses for 30 minutes – same data, 1ms response, API quota preserved.
4. Page Fragment Caching
Cache expensive page sections separately: navigation menus, sidebars, and product listings.
Instead of caching entire pages, cache the slow parts while keeping personalized content dynamic.
How to Install and Configure Memcached
Getting started is straightforward.
Installation
Ubuntu/Debian:
bash
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install memcached libmemcached-tools
CentOS/RHEL:
bash
sudo yum install memcached
Starting Memcached
bash
# Start with 256MB memory
memcached -d -m 256 -p 11211 -u memcache
Options explained:
- -d = run as daemon (background)
- -m = memory allocation in MB
- -p = port number
- -u = user account to run as
Testing Your Setup
bash
telnet localhost 11211
set testkey 0 60 5
hello
STORED
get testkey
VALUE testkey 0 5
hello
END
Memcached Best Practices
Follow these guidelines for production deployments.
Set Appropriate Expiration Times
Different data needs different TTLs:
- Static content: 24 hours
- Product listings: 1-6 hours
- User sessions: 30-60 minutes
- Real-time data: 30-60 seconds
Use Descriptive Cache Keys
python
# Bad
cache.set(‘u123’, data)
# Good
cache.set(‘user_profile_123’, data)
cache.set(‘product_page_789’, html)
Handle Cache Misses Gracefully
Always check if data exists:
python
result = cache.get(key)
if result is None:
result = database.query()
cache.set(key, result, 3600)
return result
Monitor Cache Performance
Track your hit rate regularly:
bash
echo “stats” | nc localhost 11211
Look for get_hits and get_misses. Target hit rate: 80% or higher.
Allocate Enough Memory
Start with 256MB-512MB for small sites, 1-2GB for medium traffic, 4GB+ for high-traffic applications. Watch for evictions – if they’re frequent, increase memory allocation.
Memcached for WordPress and WooCommerce
WordPress benefits hugely from object caching via Memcached.
Setup:
- Install Memcached on your server
- Add object-cache.php drop-in file
- Configure through plugins like W3 Total Cache
Performance gains:
- Database queries reduced by 70-90%
- Page load times cut by 40-60%
- Server handles 3-5x more visitors
Combine Memcached with high-quality WordPress hosting and proper server optimization for maximum results.
Conclusion
Memcached isn’t magic – it’s smart data storage. By keeping frequently accessed information in RAM, it transforms slow applications into fast ones without complicated setups.
Implementation is straightforward: install Memcached, add a client library, wrap database calls with cache checks, and watch response times drop. Whether running a blog, online store, or custom application, Memcached provides immediate performance improvements. Start with basic query caching, measure results, then expand. Need hosting optimized for Memcached?
BigCloudy’s VPS plans come pre-configured with Memcached support – enterprise-grade speed without enterprise complexity.
FAQs
Memcached caches frequently accessed data in RAM to speed up websites. Common uses include database query caching, session storage, API response caching, and page fragment caching.
Memcached stores data as key-value pairs in RAM using a slab allocator for memory management. It uses LRU (Least Recently Used) eviction when memory fills up, and distributes data across servers using consistent hashing.
Neither is universally better. Memcached excels at simple, high-throughput caching with multi-threaded performance. Redis offers data persistence and complex data structures. For basic caching, Memcached is simpler and often faster.
No. Memcached stores everything in RAM with no disk persistence. Server restarts wipe all cached data. This is intentional – Memcached is for temporary caching, not permanent storage.
No. Memcached is a cache without durability guarantees, transactions, or complex queries. It’s designed for temporary data that can be regenerated if lost.
Facebook enhanced Memcached with UDP support, connection pooling, multi-threading, and distributed clusters across regions. They created “gutter pools” for failover and used remote markers to prevent stale data across geographic locations.